Understanding the Health Gap: Using Blinder-Oaxaca Decomposition Analysis as a Health Equity Solutions Tool
May 22, 2023
Throughout Wales and the world, health inequality remains a problem that is interconnected with a wider and complex social, economic and environmental dynamic. Subsequently, action to tackle inequality in health needs to take place at a structural level, acknowledging the constraints affecting an individual or community’s capability and opportunity to enable change. While the ‘social determinants of health’ is an established concept, fully understanding the composition of the health gap is dependent on capturing the relative contributions of a myriad of social, economic and environmental factors within a quantitative analysis.
The Blinder-Oaxaca decomposition analysis sought to explain the differences in the prevalence of these outcomes in groups stratified by their ability to save at least £10 a month, whether they were in material deprivation, and the presence of a limiting long-standing illness, disability of infirmity. The analysis not only quantified the significant health gaps that existed in the years leading up to the COVID-19 pandemic, but it has also shown what determinants of health were most influential.
Understanding the factors most closely associated with disparities in health is key in identifying policy levers to reduce health inequalities and improve the health and well-being across populations.
Strategic context
Wales is a global influencer in health equity, becoming the first country to apply the milestone World Health Organization (WHO) European Health Equity Status Report initiative (HESRi) framework. The Welsh application of HESRi, is known as the Welsh Health Equity Status Report Initiative (WHESRi), aims to provide an up-to-date dynamic picture of health inequities, their burden, determinants and related policies in Wales in order to inform solutions and investment prioritisation, as well as to facilitate a joint cross-sector whole-of-government, whole-of-society policy dialogue and action towards a Healthier, More Equal and Prosperous Wales.
WHESRi uses a novel framework for understanding health equity, based on what are known as the ‘five essential conditions’ for a healthy life. These are:
- Health and Health Services
- Health and Income Security and Social Protection
- Health and Living Conditions
- Health and Social and Human Capital
- Health and Employment and Working Conditions
What is the Blinder-Oaxaca decomposition method?
The Blinder-Oaxaca decomposition analysis is a statistical method of analysis aiming to quantify the health gap in Wales, as well as to provide a better understanding of its main drivers across the five essential conditions for healthy prosperous lives for all.
In 2022, Public Health Wales published the report Influencing the Health Gap in Wales: Decomposition analysis discussion paper.The paper presents the findings of a decomposition analysis to establish the relative magnitude of influence of each of the five essential conditions on health.
What did we find out?
Notwithstanding certain limitations of the WHESRi analysis, the results show that there were significant health gaps between different population groups prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, and that the these gaps were exacerbated by the pandemic. Social and Human Capital and Income Security and Social Protection were the essential conditions accounting the most for the health gaps observed, while Health Services accounted for the least. Health gaps related to those reporting a limiting long-standing illness, disability, or infirmity remained the least explained by the method.
For example, Figure 1 shows that by decomposing the gap in prevalence of fair/poor health between those who are able to save at least £10/month and those who are not (11.5 percentage point difference), 45.5% can be explained by systematic differences in the essential conditions; and 54.5% remains unexplained. From the explained component, Income Security and Social Protection and Social and Human Capital accounts the most, 40.2% and 40.1%, respectively; while Living Conditions (7.8%) and Health Services (3.1%) accounts the least (Figure 1).
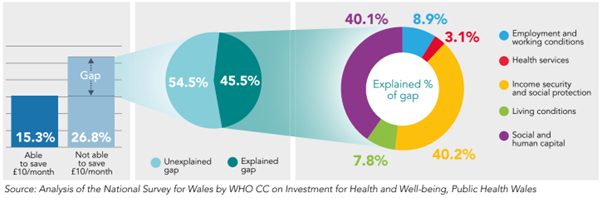
Figure 1. Decomposing the gap in prevalence of fair/poor health between those who are able to make a saving of at least £10/month, and those who are not using the Blinder-Oaxaca methodology, non-pensioner adults (aged 16-65), Wales, 2016-17 to 2019-20
Where did the data come from?
The analysis used data from The National Survey for Wales. The data was collected from 2016-17 to 2019-20, which included responses from 46,189 individuals. Three measures of self-reported health, including, prevalence of fair/poor health, low mental well-being, and low life satisfaction were captured as part of the survey and these were used to compare different population groups.
What next?
The report by Public Health Wales has shown that decomposition analysis can be used to better understand the drivers of health inequities. The findings can inform policy action, solutions and a range of multi-sector stakeholders involved in addressing health gaps and provide insights for regions around the world for applying a statistical method to better understanding health inequity. Wales will continue to link with other regions working on the HESRi to develop a better understanding of the drivers of health inequities. The next step in this process is a round-table discussion on the decomposition analysis facilitated by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre on Investment for Health and Well-being, Public Health Wales, in collaboration with key stakeholders. The event took place as part of the European Public Health Week 2023.
Influencing the Health Gap: Multi-country perspectives, webinar delivered as part of European Public Health Week, 2023
The Welsh Health Equity Status Report initiative (WHESRi) has published a new report on the Health Equity Status Report initiative (HESRi) decomposition analyses, summarising a multi-country webinar on methods and findings from Wales, Italy and Slovenia. The webinar was a solutions-focused session which explored how the application of the innovative decomposition analysis methodology has generated insights into the drivers of health inequalities.
The aims of the webinar were to:
- Share multi-country experiences on using the decomposition methodology and how it can be used as a tool to measure health equity;
- Help inform further policy action and potential solutions to reduce the health gap in Wales and beyond; and
- Gain insights into the potential next steps for action using the methodology amongst Health Equity Status Report initiative regions.
The key finding of the webinar was the need to strengthen the case for investing in well-being and health equity in Wales and beyond through policies and solution-based actions that were identified throughout the webinar.
Recording of the webinar
Further reading
• Influencing the Health Gap in Wales: Decomposition analysis discussion paper – World Health Organization Collaborating Centre On Investment for Health and Well-being (phwwhocc.co.uk)
• A detailed explanation and graphical representation of the Blinder-Oaxaca decomposition method with its application in health inequalities | Emerging Themes in Epidemiology | Full Text (biomedcentral.com)
• Health Equity Status Report initiative (who.int)
• Health Equity Dataset (shinyapps.io)